SyNeg: LLM-Driven Synthetic Hard-Negatives for Dense Retrieval
SyNeg: LLM-Driven Synthetic Hard-Negatives for Dense Retrieval
Written by. Xiaopeng Li, Xiangyang Li, Hao Zhang♢Zhaocheng Du
주요 기여 (Contributions)
- Multi-attribute Self-reflection Prompting
- LLM에게 질문-정답 쌍을 주고, 하드 네거티브 문서를 생성하도록 유도
- LLM이 생성하는 텍스트의 다양성, 품질, 정확도를 높이기 위해 self-reflection과 다중 속성 (도메인, 난이도, 길이)을 설정
- Hybrid Sampling Strategy
- LLM이 생성한 Synthetic Hard Negatives와 기존 검색 기반 네거티브를 인스턴스 단위에서 혼합
- 완전한 LLM 기반 샘플로만 학습하면 불안정한 그라디언트와 성능 저하가 발생하는데, 이를 방지
- 그라디언트 분포를 안정화시키고, 학습 수렴 및 성능을 크게 향상시킴
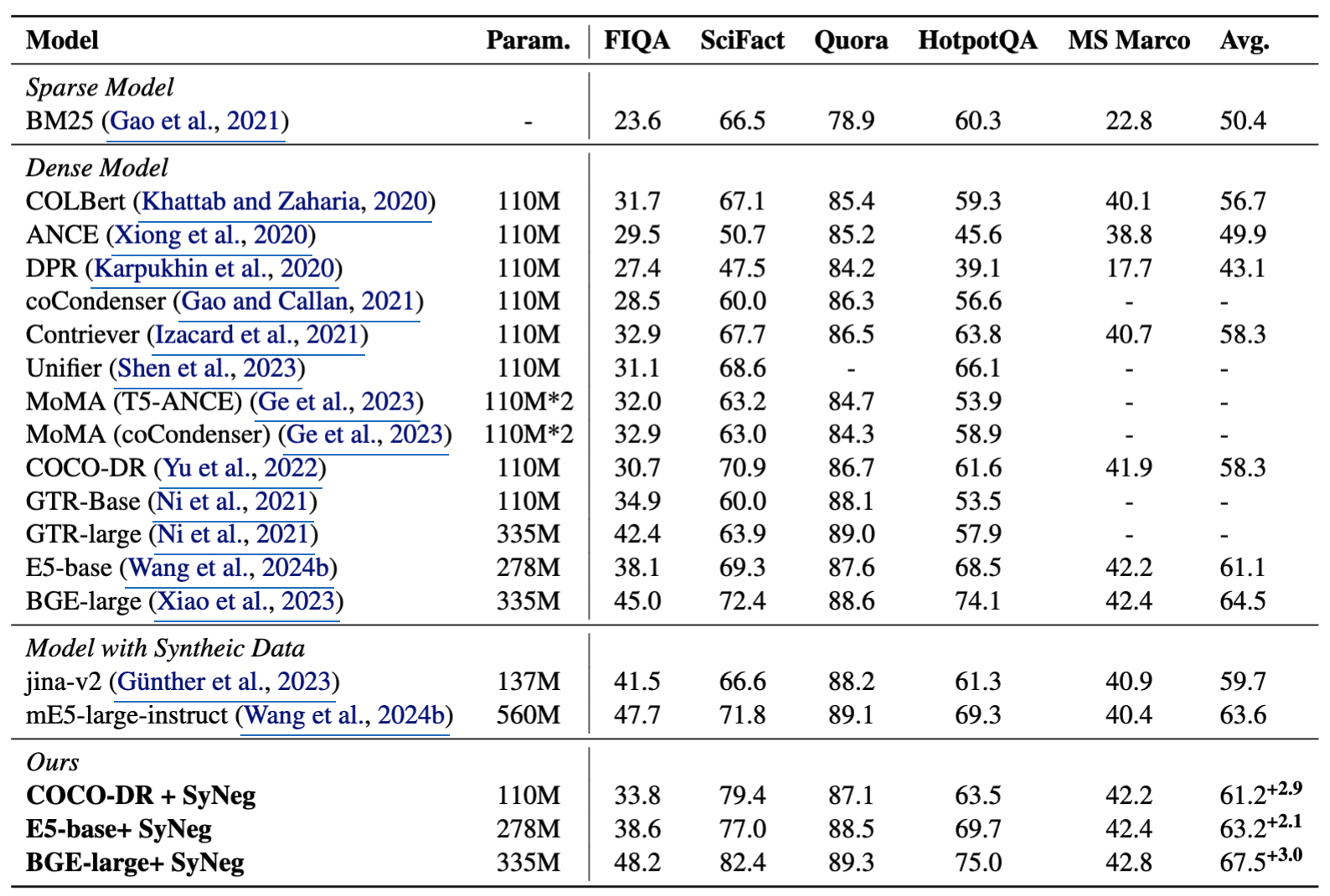
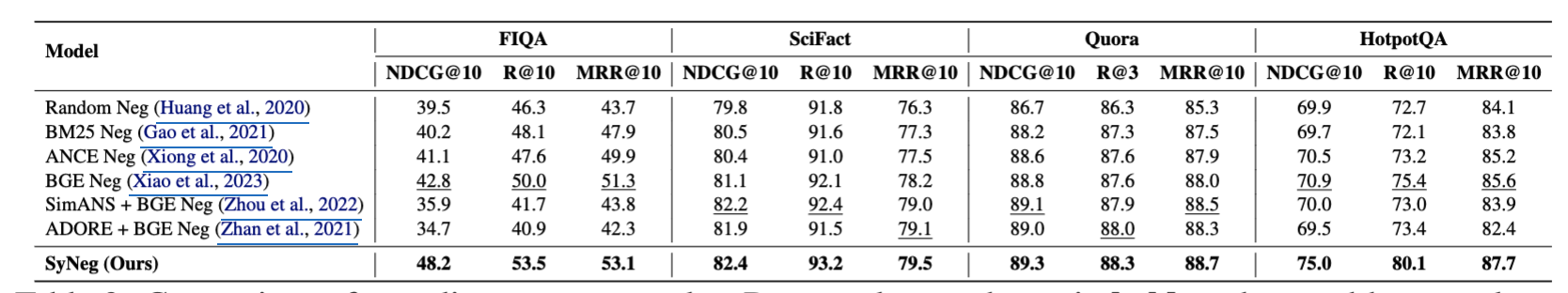
- 5개 데이터셋에서 강력한 성능 향상 입증
- BEIR 벤치마크 기반 실험에서 기존 방식 대비 2~3pt 이상 성능 향상
- 특히 SciFact, FIQA, HotpotQA 등 정보량이 많은 복잡한 질의에 대해 높은 효과
방법(Methodology)
전체 구조
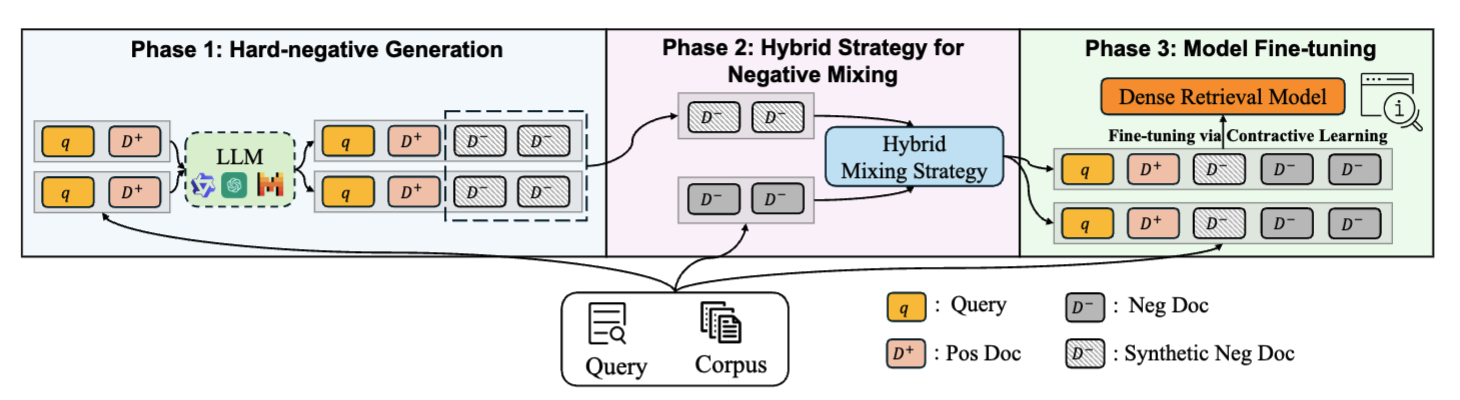
세 가지 단계로 구성됨:
- Phase 1 - Hard-negative Generation
- Phase 2 - Hybrid Strategy for Negative Mixing
- Phase 3 - Model Fine-tuning via Contrastive Learning
Phase 1: 하드 네거티브 생성
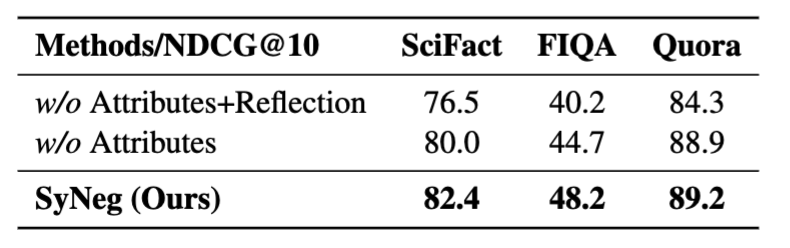
Multi-attribute Self-Reflection Prompting 전략 사용
LLM에게 다음 요소들을 조합하여 질적으로 뛰어난 하드 네거티브 생성 요구:
- Context Constraints: 하드 네거티브의 정의 및 출력 포맷(JSON) 지정
- Attributes Constraints: 도메인, 난이도, 길이 설정
- Reflection Constraints: Chain-of-Thought reasoning으로 생성 이유를 논리적으로 유도
Prompt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
Assume you are an expert in {domain_name}, and there is a example with a “user_query” and its related doc “positive_document”. example: {example} [Task Definition] ...중략... [Reasoning Definition] ...중략... [Hard Negatives Definition] ...중략... [Attributes Definition] All the negative documents should be in the education level of {difficult_level} to comprehend, and the length should be {length} the “positive_document”. [Format Definition] ...중략... =====데이터셋별로 정의 다름===== For SciFact: domain_name = [ "Epidemiology", "Public Health", "Virology", "Biostatistics", "Healthcare Policy", "Infectious Diseases", "Bioinformatics", "Medical Research", "Pharmacology" ] difficult_level = [ "Foundational (Equivalent to Elementary and Middle School)" , "Intermediate (High School and Undergraduate)" ] length = ["approximately the same as", "nearly the same as"]
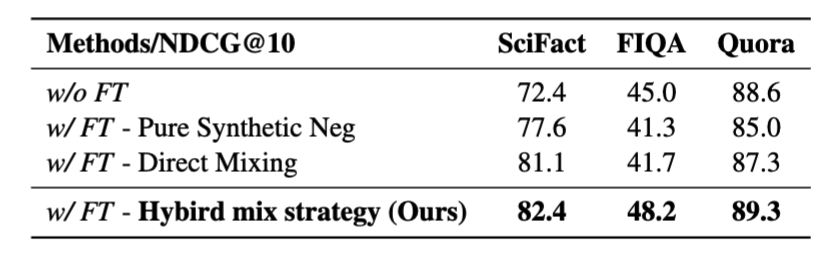
Phase 2: 하이브리드 믹싱 전략
- Direct Mix Strategy의 한계
- LLM이 만든 네거티브와 기존 네거티브를 데이터 전체 수준에서 섞음
- 어떤 쿼리는 synthetic만, 어떤 쿼리는 retrieved만 쓰일 수 있음 → 불균형, 불안정한 학습
- LLM이 만든 샘플은 너무 어려워 훈련 시 큰 gradient variance 유발 → 학습 불안정
- Hybrid Mix Strategy
- 각 쿼리-정답 쌍에 대해:
- LLM 생성 네거티브 1개 + 검색 기반 네거티브 여러 개 혼합
- 인스턴스 단위로 믹싱하여 다양한 난이도의 네거티브 포함
- 각
(query, positive_doc)쌍에 대해:예: (query, positive_doc, [synthetic_neg_1, retrieved_neg_1, retrieved_neg_2])- LLM이 생성한 synthetic hard negative 1개 추가
- 기존 retriever (예: BGE, BM25, ANCE 등)로 가져온 hard negative N개 추가
→ 이들을 한 인스턴스에 같이 포함시켜 학습에 사용합니다.
- 즉, 모든 query에 대해 최소 1 synthetic negative + 여러 retrieved negatives 포함됨
- 각
- 각 쿼리-정답 쌍에 대해:
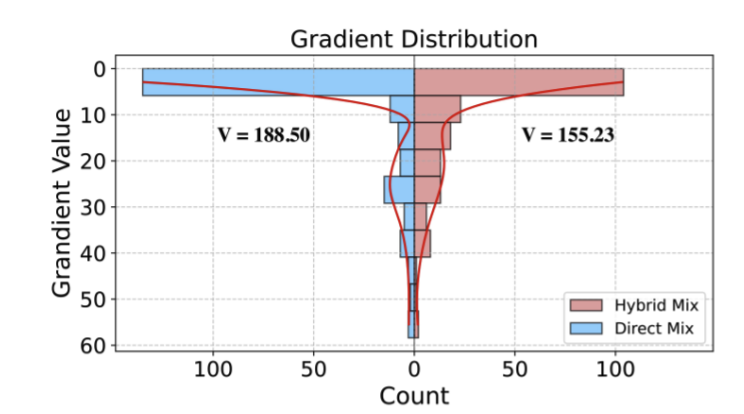
Gradient 안정화 실험
- Hybrid Mix는 Direct Mix 대비 분산(V)이 작음 (155.23 vs. 188.5)
Phase 3: 모델 파인튜닝
\[\mathcal{L} = -\log\frac{f(q, d^+)}{f(q, d^+) + \sum_{d^- \in D^-_h} f(q, d^-)}, \quad f(q, d) = \exp\left(\frac{s(q, d)}{\tau}\right)\]- Loss Function: InfoNCE 기반 contrastive loss
- $D^-_h$: 하이브리드 네거티브 집합 (synthetic + 검색 기반)
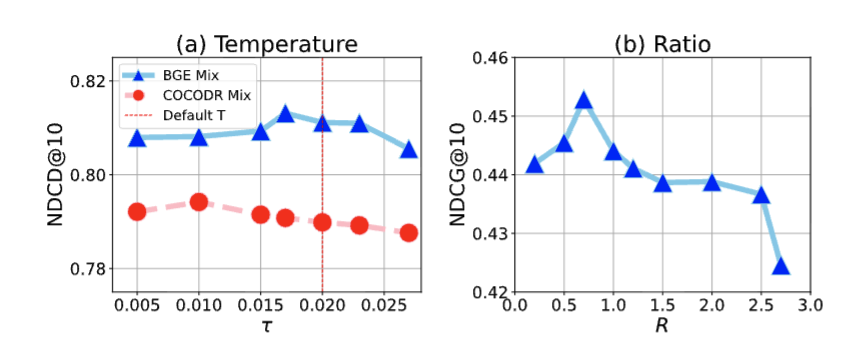
하이퍼파라미터 분석
- Temperature (τ)
- 낮을수록 긍정/부정 간 대비 증가 → 성능 향상
- Optimal: BGE → 0.017, COCO-DR → 0.01
- Synthetic Negative 비율 (R)
- 너무 많으면 오히려 성능 저하
- 최적: 약 0.7배 수준이 가장 좋은 성능을 보임
성능 요약
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.